Your home’s large refrigerators must work without pause. A standard refrigerator uses between 300 and 800 watts for power, which means it operates at 3 to 6 amps under 120 volts. The knowledge of power consumption helps you control your electricity usage.
Your household refrigerator runs continuously, which impacts your electricity charges. Because refrigerators operate without interruption, their power consumption builds over time. A comprehensive grasp of power usage is essential to saving money and energy.
Every home needs a refrigerator, but this essential device draws substantial watts from the power grid. Assessing the power usage of household appliances enables you to decide when solar panels are needed or alternative measures for cost reduction. This decision brings positive benefits towards reduced energy consumption.
What Are Refrigerator Amps?
The compressor electrical power required for cold preservation in a refrigerator operates under refrigerator amps. Home refrigerator systems operate between 3 and 5 amps on 120-volt power. A 15- to 20-amp dedicated circuit is required because in-rush amperage levels are higher.
Due to sporadic operation, the refrigerator’s average amperage has decreased. Professionals measure this usage through kilowatt-hour data (kWh). A study of refrigerator amps helps you see how your appliance uses energy throughout time.
“Refrigerator Power Consumption: Wattage Breakdown by Period”
Here’s a table showing the average energy consumption of a refrigerator in kWh based on different periods:
| Period | Power Consumption (Watts) | Estimated Energy Use (kWh) |
| Hourly | 100 – 400 Watts | 0.1 – 0.4 kWh |
| Daily | 300 – 800 Watts | 0.6 – 1.6 kWh |
| Monthly | 300 – 800 Watts | 18 – 24 kWh |
| Yearly | 300 – 800 Watts | 220 – 300 kWh |
Evaluating your refrigerator’s electricity consumption requires understanding the kWh, the unit of measurement on your electric bill. By determining your refrigerator’s electricity usage, you can better predict its effect on your monthly expenses.
How many volts and amps does a refrigerator use?
To calculate your fridge’s voltage and amperage using its Energy Guide label, follow these steps:
1: Translate kWh to watthours (Wh): To convert the kWh on your Energy Guide label value to watthours (Wh), multiply it by 1000. For example, the energy profile on the label indicates 630 kWh, so multiply this number by 1,000 to get 630,000 Wh.
2: Find the daily wattage: The process requires verifying total watt-hours over 365 days to determine daily wattage. For example, 630,000 Wh ÷ 365 = 1,726 Wh per day.
3: Calculate hourly wattage: Divide daily power by 24 hours. For example, 1,726 Wh ÷ 24 = 72 W per hour.
4: Determine amperage: Refrigerators typically use 120-volt outlets. The hourly amperage is calculated by dividing the hourly wattage by 120 volts. Example: 72 W ÷ 120 V = 0.60 amps.
Using this formula allows you to discover the precise amperage (0.60 amps) and voltage (120 V) that your refrigerator requires
Buy an Energy Meter to Measure Power Consumption:
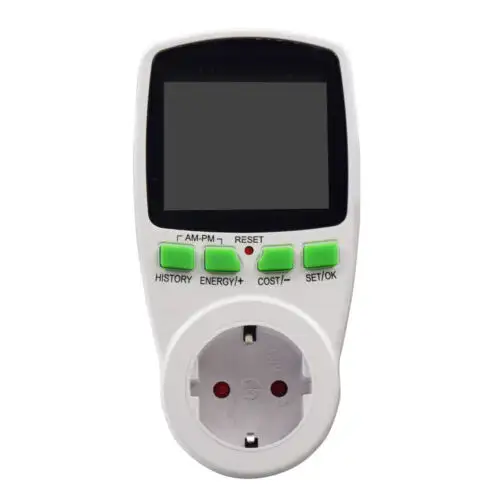

Your fridge’s power use measurement can be achieved through using an energy meter. A compact power monitoring device serves as a plug-in accessory for refrigerators to track their electricity consumption. This equipment displays instantaneous watt data along with kWh readings from your fridge.
The utilization and operation of energy meters create a simple system. Simply insert the device between your refrigerator and power outlet, then review the displayed results. Understanding your fridge’s energy usage becomes possible through this testing method, which collects usage data to help you control your electricity expenses.
Energy meters exist at affordable prices combined with uncomplicated usage methods. The devices display total kilowatt-hour (kWh) energy utilization statistics, while certain products also provide estimated cost information. Anyone searching to save energy alongside refrigerator power estimation can use this measurement device successfully.
How Many Amps Does a Mini Fridge, Freezer, or Refrigerator Use?
The number of amps a mini fridge, freezer, or refrigerator uses depends on its size and features. Here’s a quick comparison:
| Refrigerator Types | Refrigerator Wattage | Actual Energy Usage (Around ⅓ of refrigerator wattage) | Amps (= Watts / Volts) |
| Mini Fridge | 50W to 100W | 16W to 34W | 0.42 to 0.83 amps |
| Household Refrigerator | 500W | 167W | 1.39 amps |
| Standard Refrigerator | 100W to 800W | 33W to 266W | 0.83 to 6.67 amps |
| Freezer | 100W to 400W | 33W to 133W | 0.83 to 3.33 amps |
| Large Commercial Freezer | 700W to 2000W | 233W to 667W | 5.83 to 16.67 amps |
| Energy-Efficient Refrigerator | 150W to 300W | 50W to 100W | 0.42 to 0.83 amps |
“Refrigerator Startup Amps: How Much Power Does It Draw?”
A standard 480W refrigerator requires sudden power consumption at startup equal to 1440W with a draw of 24 amps before stabilizing. Installations exhibit a startup power 480W with a 4-amperage draw following regular operation.
The starting power surge at startup exceeds the typical power draw of running operations. The beginning of compressor operation demands additional power because it must initialize the cooling procedure. The refrigerator power draws normal amounts after the compressor begins its operation.
Startup Watts vs. Running Watts
The power demand required to start a refrigerator’s compressor operating after complete shutdown is known as startup watts. Powder surge levels reach twice to thrice higher than the standard power operating level. Regular operation of your refrigerator pulls 167W but startup wattage can surge to 500W. A few seconds is the duration of the power surge however, it requires a robust power source to manage this peak consumption.
Once the compressor runs continuously, the refrigerator utilizes running watts as its operating power. During functioning times, these appliances use power between 100W and 800W that maintains a consistent supply to the refrigerator.
| Running Watts | 120V x 3A | 360W |
| Startup Watts | 360W x 3 | 1080W |
Startup Amps vs. Running Amps
As the refrigerator powers on, startup amps reach levels much beyond running current levels. During startup operations, the refrigerator draws power between 5 and 7 times more than its operating current. The peak startup amperes can exceed 21 amps when the refrigerator starts (3A * 7).
When the refrigerator enters its normal operational state, it reduces its amperage to reach its steady-running amps. Understanding these two different amp types is essential for finding the proper power supply for your refrigerator.
Tips to Save Your Electricity Bill
Saving energy must be a priority because households typically spend 16.41 cents per kWh for electricity. Here are some practical ways to save on your electricity bill.
Set your refrigerator’s temperature right: Keep your fridge between 35°F (1.6°C) and 38°F (3.3°C) and your freezer at 0°F (-17.7°C). The proper temperature setting helps your food stay fresh without requiring unnecessary power.
Consider Solar Energy: Solar energy can power your refrigerator and high-wattage appliances like air conditioners and microwaves. It’s an eco-friendly way to lower your electricity bill.
Clean Your Refrigerator’s Condenser Coil: General coil cleaning reduces energy usage by 30%. Your refrigerator will operate more efficiently.
Ventilate Appliances Properly: Place your refrigerator and other large appliances in areas that receive good air circulation. Ventilation dramatically reduces the compressor’s operational stress, increasing its energy efficiency.
Solar Generators for Refrigerators
If you’re interested in using solar energy, Jackery Solar Generators are powerful and portable. They can provide high power output to run your refrigerator and other essential appliances. These generators are compatible with Jackery SolarSaga Solar Panels, which use monocrystalline silicon cells to capture sunlight and convert it into usable electricity for appliances.
Conclusion
The power consumption of typical refrigerators falls between 3 and 6 amps when in normal use. Your refrigerator consumes exceptional amounts of power when the device starts up but requires between 3 and 6 amps for normal operation. Knowledge of this pattern enables better planning for your power system design.
Conserving energy becomes easier by maintaining your refrigerator at its proper temperature settings and performing routine coil maintenance. In the future, combining energy-conserving appliances with solar power systems will reduce electricity costs.
FAQs About Refrigerator
Q1. Can I run a fridge on a 15 amp?
Yes, you can run a fridge on a 15-amp circuit if the fridge size is standard. However, you would find a 20-amp circuit for most larger or energy-hungry refrigerators.
Q2. Is a fridge 5 amp or 15 amp?
The typical running amps for a fridge are between 3 and 6. The amps at startup, however, may be several times larger, often between 5 and 7 times the running amps.
Q3. How many amps does a refrigerator draw?
A refrigerator draws about 3 to 6 amps in normal operation. However, it can draw 5 to 7 times more amps when starting up.
Q4. Does a fridge need a 20-amp circuit?
A fridge usually requires a 15-amp or 20-amp dedicated circuit. The larger refrigerators with extra features may require the higher 20-amp circuit.
Q5. Is five amps enough for the fridge?
Yes, five amps is usually enough to run most standard fridges. However, the startup amps could be a bit higher at startup.